Rspamd statistic settings
Introduction
Rspamd utilizes statistics to determine the classification of messages into either spam or ham categories. This classification process is based on the Bayesian theorem, which combines probabilities to assess the likelihood of a message belonging to a particular class, such as spam or ham. The following factors play a role in determining this probability:
- the probability of a specific token to be spam or ham (which means efficiently count of a token’s occurrences in spam and ham messages)
- the probability of a specific token to appear in a message (which efficiently means frequency of a token divided by a number of tokens in a message)
Statistics Architecture
However, Rspamd employs more advanced techniques to combine probabilities, including sparsed bigrams (OSB) and the inverse chi-square distribution.
The OSB algorithm goes beyond considering single words as tokens and instead takes into account combinations of words, taking into consideration their positions. This schema is visually represented in the following diagram:
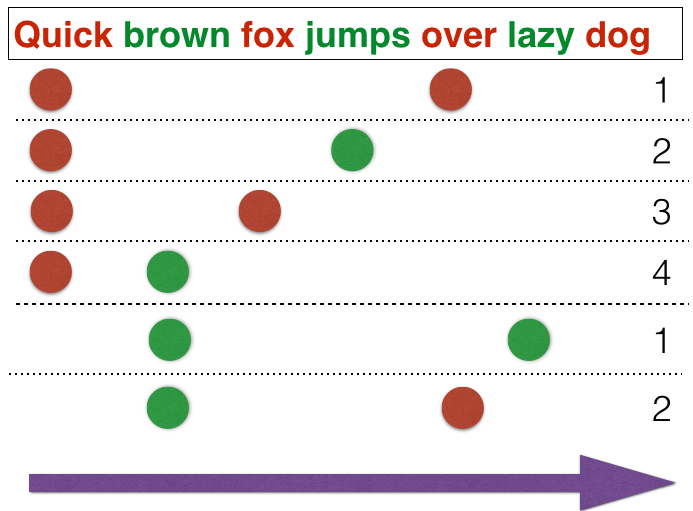
The main drawback of this approach is the increased number of tokens, which is multiplied by the size of the window. In Rspamd, we use a window size of 5 tokens, resulting in the number of tokens being approximately 5 times larger than the number of words.
Statistical tokens are stored in statfiles, which are then mapped to specific backends. This architecture is visually represented in the following diagram:
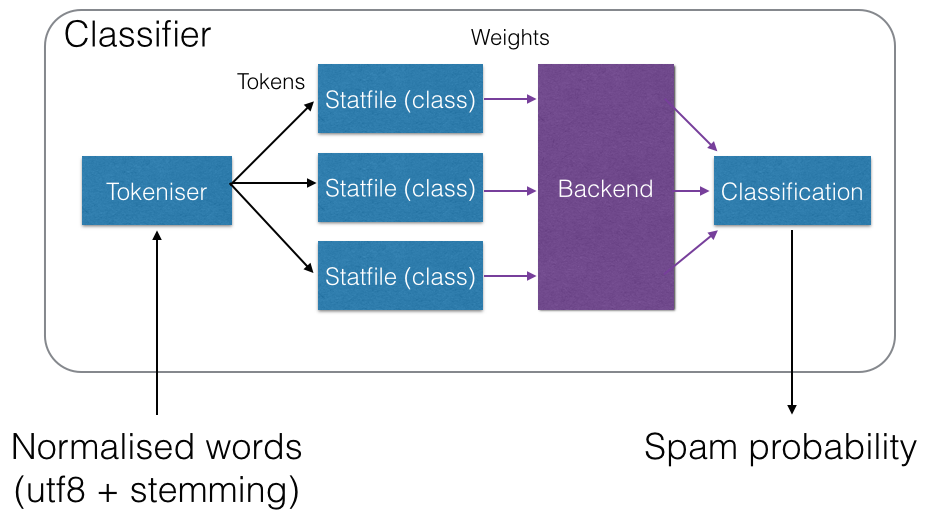
Statistics Configuration
Starting from Rspamd 2.0, we recommend using redis as the backend and osb as the tokenizer, which are set as the default settings.
The default configuration settings can be found in the $CONFDIR/statistic.conf file.
classifier "bayes" {
# name = "custom"; # 'name' parameter must be set if multiple classifiers are defined
tokenizer {
name = "osb";
}
cache {
}
new_schema = true; # Always use new schema
store_tokens = false; # Redefine if storing of tokens is desired
signatures = false; # Store learn signatures
#per_user = true; # Enable per user classifier
min_tokens = 11;
backend = "redis";
min_learns = 200;
statfile {
symbol = "BAYES_HAM";
spam = false;
}
statfile {
symbol = "BAYES_SPAM";
spam = true;
}
learn_condition = 'return require("lua_bayes_learn").can_learn';
# Autolearn sample
# autolearn {
# spam_threshold = 6.0; # When to learn spam (score >= threshold)
# ham_threshold = -0.5; # When to learn ham (score <= threshold)
# check_balance = true; # Check spam and ham balance
# min_balance = 0.9; # Keep diff for spam/ham learns for at least this value
#}
.include(try=true; priority=1) "$LOCAL_CONFDIR/local.d/classifier-bayes.conf"
.include(try=true; priority=10) "$LOCAL_CONFDIR/override.d/classifier-bayes.conf"
}
.include(try=true; priority=1) "$LOCAL_CONFDIR/local.d/statistic.conf"
.include(try=true; priority=10) "$LOCAL_CONFDIR/override.d/statistic.conf"
You are also recommended to use bayes_expiry module to maintain your statistics database.
Please note that classifier-bayes.conf is include config of statistic.conf which created for user’s simplicity.
For most of setups where there is only one classifier is used - classifier-bayes.conf is suffient and statistic.conf should be leaved unmodified.
If you need describe multiply different classifiers - then you need create local.d/statistic.conf, that should describe classifier sections, each classifier must have own name and have all options from default config, as there will be no fallback. Common usecase for such case is when first classifier is per_user and second is not.
Classifier and headers
The classifier in Rspamd learns headers that are specifically defined in the classify_headers section of the options.inc file. Therefore, there is no need to remove any additional headers (e.g., X-Spam) before the learning process, as these headers will not be utilized for classification purposes. Rspamd also takes into account the Subject header, which is tokenized according to the aforementioned rules. Additionally, Rspamd considers various meta-tokens, such as message size or the number of attachments, which are extracted from the messages for further analysis.
Redis statistics
Supported parameters for the Redis backend are:
Required parameters
name: Unique name of the classifier. Must be set when multiple classifiers are defined; otherwise, optional.tokenizer: Currently, only OSB is supported. Must be set as shown in the default configuration.new_schema: Must be set totrue.backend: Must be set to"redis".learn_condition: Lua function that verifies that learning is needed. The default function must be set if you have not written your own. Omittinglearn_conditionfromstatistic.confwill lead to losing protection from overlearning.servers: IP or hostname with a port for the Redis server. Use an IP for the loopback interface if you have defined localhost in /etc/hosts for IPv4 and IPv6, or your Redis server will not be found!min_tokens: Minimum number of words required for statistics processing.statfile: Defines keys for spam and ham mails.
Optional parameters
write_servers: For write-only Redis servers (usually masters).read_servers: For read-only Redis servers (usually replicas).password: Password for the Redis server.db: Database to use, must be a non-negative integer (though it is recommended to use dedicated Redis instances and not databases in Redis).min_learns: Minimum learn to count for both spam and ham classes to perform classification.autolearn {}: This section defines the behavior of automatic learning for spam and ham messages based on specific thresholds and balance settings. It includes the following options:spam_threshold(No default value): Specifies the score threshold above which a message is considered spam and is eligible for automatic spam learning. If a message’s score exceeds this threshold, it will be learned as spam. If not set, autolearning for spam will depend on the verdict of the message.ham_threshold(No default value): Specifies the score threshold below which a message is considered ham and is eligible for automatic ham learning. If a message’s score is below this threshold, it will be learned as ham. If not set, autolearning for ham will depend on the verdict of the message.check_balance(Default:true): Enables checking of the balance between spam and ham learns. If the balance is too skewed, learning will be skipped based on the ratio defined bymin_balance.min_balance(Default:0.9): Ensures balance between spam and ham learns. If the ratio of spam learns to ham learns (or vice versa) exceeds1 / min_balance, learning for the more frequent type is skipped until the other type catches up. For example, with the default value of0.9, learning is skipped if one type exceeds the other by a ratio of approximately1.11(1/0.9). This helps prevent bias in the learning process.
For further details, see the Autolearning section.
per_user: For more details, see the Per-user statistics section.cache_prefix: Prefix used to create keys where to store hashes of already learned IDs, defaults to"learned_ids".cache_max_elt: Amount of elements to store in onelearned_idskey.cache_max_keys: Amount oflearned_idskeys to store.cache_elt_len: Length of hash to store in one element oflearned_ids.
Autolearning
Starting from version 1.1, Rspamd introduces autolearning functionality for statfiles. Autolearning occurs after all rules, including statistics, have been processed. However, it only applies if the same symbol has not already been added. For example, if BAYES_SPAM is already present in the checking results, the message will not be learned as spam.
There are three options available for specifying autolearning:
autolearn = true: autolearning is performing as spam if a message hasrejectaction and as ham if a message has negative scoreautolearn = [-5, 5]: autolearn as ham if the score is less than-5and as spam if the score is more than5autolearn = "return function(task) ... end": use the following Lua function to detect if autolearn is needed (function should return ‘ham’ if learn as ham is needed and string ‘spam’ if learn as spam is needed, if no learning is needed then a function can return anything includingnil)
Redis backend is highly recommended for autolearning purposes due to its ability to handle high concurrency levels when multiple writers are synchronized properly. Using Redis as the backend ensures efficient and reliable autolearning functionality.
Per-user statistics
To enable per-user statistics, you can add the per_user = true property to the configuration of the classifier. However, it is important to ensure that Rspamd is called at the final delivery stage (e.g., LDA mode) to avoid issues with multi-recipient messages. When dealing with multi-recipient messages, Rspamd will use the first recipient for user-based statistics.
Rspamd prioritizes SMTP recipients over MIME ones and gives preference to the special LDA header called Delivered-To, which can be appended using the -d option for rspamc. This allows for more accurate per-user statistics in your configuration.
You can change per-user statistics to per-domain (or any other) by utilizing a Lua function. The function should return the user as a string or nil as a fallback. For example:
per_user = <<EOD
return function(task)
local rcpt = task:get_recipients('any')
if rcpt then
local first_rcpt = rcpt[1]
if first_rcpt['domain'] then
return first_rcpt['domain']
end
end
return nil
end
EOD
Sharding
Starting from version 3.9, per-user statistics can be sharded across different Redis servers using the hash algorithm.
Example of using two stand-alone master shards without read replicas:
servers = "hash:bayes-peruser-0-master,bayes-peruser-1-master";
Example of using a setup with three master-replica shards:
write_servers = "hash:bayes-peruser-0-master,bayes-peruser-1-master,bayes-peruser-2-master";
read_servers = "hash:bayes-peruser-0-replica,bayes-peruser-1-replica,bayes-peruser-2-replica";
Important notes:
- Changing the shard count requires dropping all Bayes statistics, so please make decisions wisely.
- Each replica should have the same position in
read_serversas its master inwrite_servers; otherwise, this will result in misaligned read-write hash slot assignments. - You can’t use more than one replica per master in a sharded setup; this will result in misaligned read-write hash slot assignments.
- Redis Sentinel cannot be used for a sharded setup.
- In the controller, you will see incorrect
Bayesian statisticsfor the count of learns and users.